At the turn of the 20th century, the valve bag was invented by Adelmer M. Bates, a salesman of salt. The story is that he was selling more salt than his company could deliver, and the filling method of the day seemed to limit his sales commissions. Once the bag was developed, Mr. Bates then started a venture to develop equipment to fill his new bag.
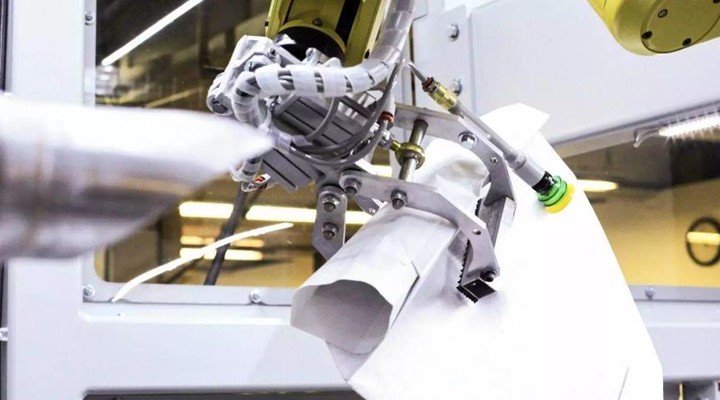
This led to the development of valve bag packers, also known as valve packers or valve bag filling machines, which notably handle a wide range of dry bulk materials, such as powders, granules, and pellets.
Table of Content
- Why Choose a Valve Bagger
- Main Advantages of Valve Bag Fillers
- What Types of Valve Baggers exist?
- Air Packer
- Auger Packer
- Gravity Packer
- Impeller Packer
- Vacuum Packer
- How to Choose the Right Valve Bagging Equipment
- 11 Key Factors to Consider when Choosing the Right Packer
Why Choose a Valve Bagger?
Though many granular or pelleted products can be effectively filled into valve bags, the largest use of?valve bags have centered around powdered products or mixes including powders. Because the opening of a valve bag is much smaller than that of an open mouth bag, the flow of the powdered product can be better controlled.
The earliest advantage of valve bags was that they were self-closing and reduced the labor required to fill and close (hand sew) the open mouth sacks of the day.
Despite many innovations in the valve design including film lock and double trap, the self-closing feature is far from a hermetic seal. For this reason, many of the bags used in the chemical and food industry are ultrasonically sealed after filling.
Other advantages of the valve bag include a more tightly filled bag and a squarer bag that will often make a better stack on the pallet (in comparison to other bag forms like open mouth and form-fill-seal).
Here are some of the key advantages of using valve bag filling equipment:
- Precise and consistent filling
- Reduce risk of contamination
- Bag integrity
- Efficient packaging
- Dust control
- Versatility
- Reduced material waste
- Consistent bag appearance
- Quick changeover
- Quality assurance
- Increased productivity
- Remote monitoring and control
Overall, valve packers provide a cost-effective and efficient solution for packaging dry bulk materials while offering numerous advantages related to accuracy, cleanliness, versatility, and productivity.
What Types of Valve Baggers Exist?
Valve bag filling machines come in various types and configurations to accommodate different industries, production requirements, and materials. Below are some of the common types of valve baggers.
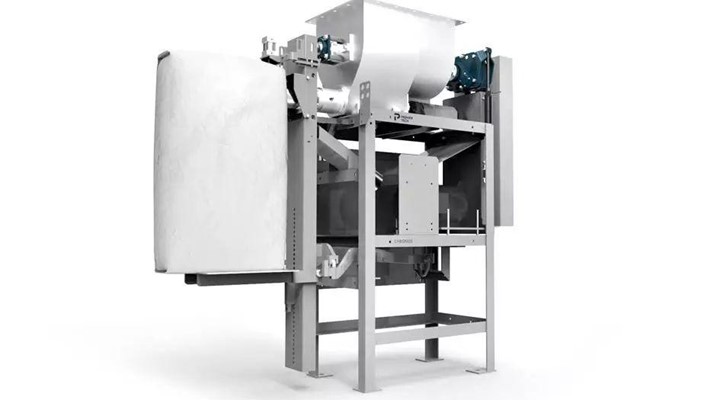
Air Packer Valve Baggers
Air packer bagging machines also known as Force Flow use compressed air to fluidize and fill valve bags with powdered or fine materials.
They are commonly used for filling materials that are food grade, as no moving parts are in contact with the product, as well as materials that tend to be dusty, such as cement.
Pros
- Fast fill
- Good accuracy
- Simple and reliable
- Versatile – works with fine powders and products with particle sizes up to 3/8”
- No moving parts in product stream
- Gentle handling of product – no mechanical shearing, minimal degradation
- Easy to clean out – drop bottom and chamber is accessible
Cons
- Adds air to product during fill
- Risk of bursting a bag as bag is filled under pressure
- Does not handle very light products well (<10 pounds per cubic foot)
- Does not handle “sticky” products well (like bakery mixes with fat content)
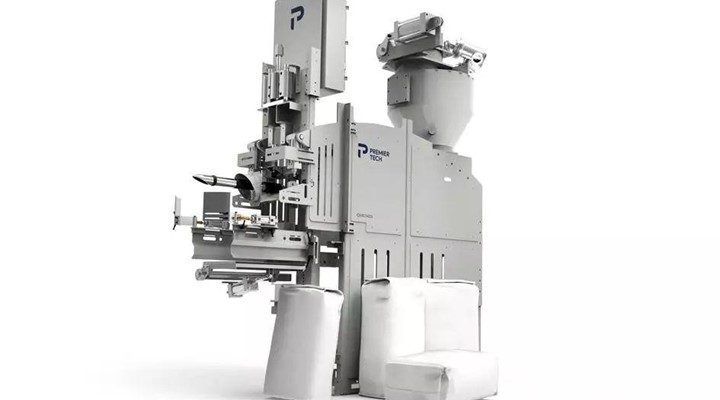
Auger Valve Baggers
Auger valve bag fillers use an auger (screw conveyor) to measure and dispense powdered or granular materials into valve bags. They are suitable for fine and free-flowing materials like cement, flour, and chemicals.
Pros
- Little air is added to the product during fill
- Rarely bursts a bag as the bag is not filled under pressure
- Few adjustments – easily understood mechanical fill method
- Versatile - will handle a wide range of products – including difficult “sticky” products like bakery mixes with fat content
Cons
- May require violent settling to tightly fill a bag
- Fluidized powders can flood past the auger even when the auger is stopped
- Typically slower than other filling methods
- Few ways to tune the machine to ideal settings for multiple products
- Subject to abrasion – wearing components in the product stream
- Can cause mechanical shearing and degradation of product
Gravity Valve Baggers
Gravity valve baggers rely on the force of gravity to fill valve bags with granular materials like grains, seeds, and fertilizers. They are relatively simple and cost-effective.
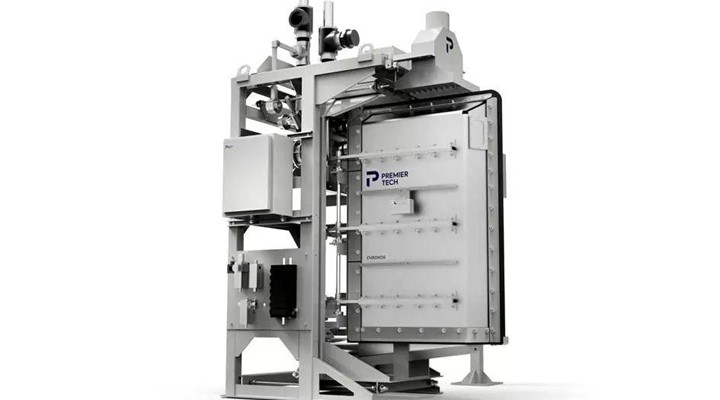
Impeller Packer
Impeller valve bag fillers or Jet Flow use a rotating impeller or paddle wheel to dispense materials into valve bags. They are versatile and suitable minerals like lime, talc, gypsum, clay and cement.
Pros
- Fast filling of most powders
- Tightly filled bags
- Low-cost solution for non-food products
Cons
- Limited product range – 200 mesh and finer particle size
- Difficult to clean (prior to a product changeover)
- Subject to abrasion – wearing components in the product stream
- Can cause mechanical shearing and degradation of product
- Adds air to product during fill
- Risk of bursting a bag as bag is filled under pressure
- Some products can cause heat in the impeller housing – product scorching is possible
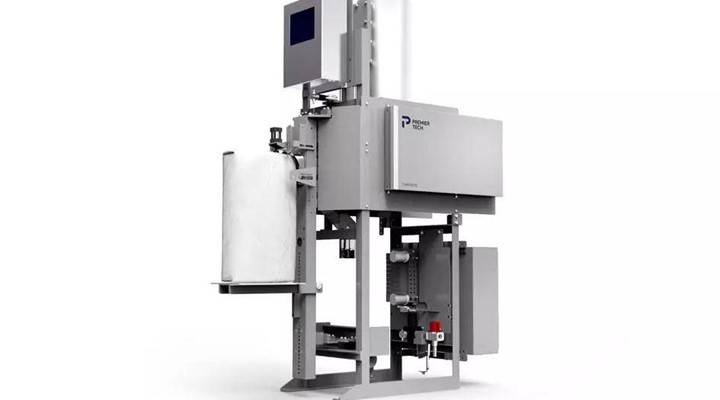
Vacuum Packer
Vacuum valve bag fillers package ultra-fine powders compacted in porous valve bags. The vacuum chamber draws the product inside the bag at uniform rates while containing dust emissions.
This filling method ensures a clean working environment and is suitable for powdery chemicals like carbon black, fumed alumina, and pigments.
Pros
- Handles very light products well (< 10 pounds per cubic foot)
- Produces tightly compressed bags that are stable when stacked
- Gentle handling of product – no mechanical shearing, minimal degradation
- No moving parts in product stream
- If a bag bursts during fill, product is contained in vacuum chamber – environment remains clean
Cons
- Difficult to fill into a bag that has a poly barrier ply
- Slow fill
- Expensive compared to other filling methods
- Can burst bags during fill
The choice of the most suitable type of valve bagger depends on factors like the type of material being packaged, production capacity, bag type, and specific industry requirements.
Valve bag manufacturers and suppliers often offer various configurations and customization options to meet the diverse needs of their customers.
11 Key Factors to Consider when Choosing the Right Packer
Choosing the best valve bag packer for your specific needs requires careful consideration of several factors. To assist with your choice, here are some key factors to consider when making your selection:
1. Material Compatibility
Ensure that the valve bag packer you choose is compatible with the type of material you will be filling.
Consider the material's characteristics, such as flowability, abrasiveness, and moisture content, as these can impact the choice of equipment.
2. Throughput Capacity
Determine your required production rate or throughput capacity. Different valve bag packers have varying capacities, so it's important to select one that can meet your production demands.
3. Bag Size and Type
Consider the size and type of valve bags you will be using. Ensure that the equipment is designed to handle the bag dimensions and materials you intend to use.
4. Accuracy and Precision
Evaluate the level of accuracy and precision required for your filling process. Some applications demand high accuracy, while others may allow for a certain level of variance. Choose a valve bagger that can meet your accuracy requirements.
5. Safety Features
Prioritize safety features such as emergency stop buttons, safety interlocks, and guarding to protect operators during operation and maintenance.
6. Dust Control and Containment
Dust control is crucial, especially when dealing with dusty materials. Look for features like dust collection systems and sealing mechanisms to minimize dust emissions and ensure a clean working environment.
7. Ease of Operation and Maintenance
Consider the ease of operating and maintaining the valve bag packer. User-friendly controls, accessibility for maintenance, and readily available spare parts can make a significant difference in long-term efficiency.
8. Flexibility and Versatility
Assess whether the valve bag packer can handle a variety of products or if it's designed for a specific type of material. A versatile machine can be more cost-effective in the long run.
9. Footprint and Space Requirements
Consider the available space in your facility. Ensure that the valve bag packer can fit within your layout and meet any space constraints. Some valve bag manufacturers use 3D software that can place the bagger in your environment to ensure it fits and is installed in the best place possible.
10. Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
Compare the initial cost of the equipment with the expected ROI. Consider factors like increased production efficiency, reduced labor costs, and decreased material waste when calculating ROI.
11. Future Expansion and Upgrades
Consider whether the equipment can accommodate future growth and whether it can be easily upgraded or modified to meet changing production requirements.
































-205x205.jpg)


